Uses of wrought iron
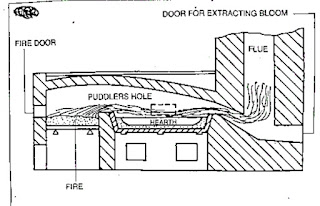
Wrought iron manufacturing process of wrought iron . properties and uses of wrought iron Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. The analysis of wrought iron shows as much as 99.9% of iron. When heated, wrought iron does not melt, but only becomes pasty and in this form it can be forged to any shape. Modern methods used to produce wrought iron in large quantities are the -pudding process -aston or byers process Pudding process Wrought iron is manufactured by refining pig-iron. By refining pig-iron silicon is removed completely, a greater amount of phosphorus is removed, and graphite is converted to combined carbon. The above process is carried out in a pudding furnace. Pudding furnace This furnace is a coal-fired reverberatory furnace. The term reverberatory is applied because the charge is not in actual contact with the fire, but receives its heat by reflection from the dome shaped furnace roof. The product obtained is taken out from the furnace in the form of balls (or blooms) havin...








